前言
写本文的初心是实现开机自启动app的功能,即Apple官方说的:An app with this key is also relaunched in the background immediately after system boot to ensure that the VoIP services are always available.
正文
- Legacy VoIP background mode is deprecated and no longer supported
https://forums.developer.apple.com/thread/50106
#import <PushKit/PushKit.h>
PushKit
- PushKit notifications offer the following advantages over user notifications:
https://help.apple.com/xcode/mac/current/#/devdfd3d04a1
<!-- https://developer.apple.com/documentation/pushkit/pkpushregistry -->
func registerForVoIPPushes() {
self.voipRegistry = PKPushRegistry(queue: nil)
self.voipRegistry.delegate = self
self.voipRegistry.desiredPushTypes = [PKPushTypeVoIP]
}
NSObject+debugCheck.h
//
// NSObject+debugCheck.h
// Reverse Me
//
// Created by Derek Selander on a happy day.
// Copyright (c) 2013 Derek Selander. All rights reserved.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/sysctl.h>
#include <string.h>
@interface NSObject (debugCheck)
#define SEC_IS_BEING_DEBUGGED_RETURN_VOID() size_t size = sizeof(struct kinfo_proc); \
struct kinfo_proc info; \
int ret, name[4]; \
memset(&info, 0, sizeof(struct kinfo_proc)); \
name[0] = CTL_KERN; \
name[1] = KERN_PROC; \
name[2] = KERN_PROC_PID; \
name[3] = getpid(); \
if ((ret = (sysctl(name, 4, &info, &size, NULL, 0)))) { \
if (ret) return; \
} \
if (info.kp_proc.p_flag & P_TRACED) return
#define SEC_IS_BEING_DEBUGGED_RETURN_NIL() size_t size = sizeof(struct kinfo_proc); \
struct kinfo_proc info; \
int ret, name[4]; \
memset(&info, 0, sizeof(struct kinfo_proc)); \
name[0] = CTL_KERN; \
name[1] = KERN_PROC; \
name[2] = KERN_PROC_PID; \
name[3] = getpid(); \
if ((ret = (sysctl(name, 4, &info, &size, NULL, 0)))) { \
if (ret) return nil; \
} \
if (info.kp_proc.p_flag & P_TRACED) return nil
@end
see also
<!-- 为VoIP应用提供了后台socket连接,定期唤醒并且随开机启动的权限 -->
Implementing a VoIP App
A Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) app allows the user to make phone calls using an Internet connection instead of the device’s cellular service. Such an app needs to maintain a persistent network connection to its associated service so that it can receive incoming calls and other relevant data. Rather than keep VoIP apps awake all the time, the system allows them to be suspended and provides facilities for monitoring their sockets for them. When incoming traffic is detected, the system wakes up the VoIP app and returns control of its sockets to it.
To configure a VoIP app, you must do the following:
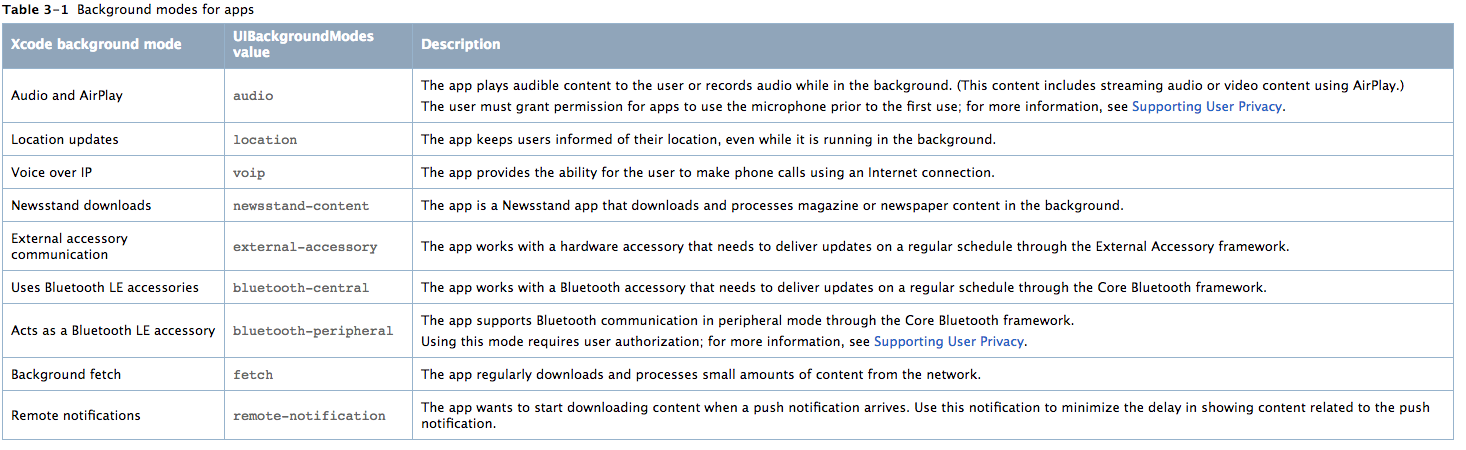
1、Enable support for Voice over IP from the Background modes section of the Capabilities tab in your Xcode project. (You can also enable this support by including the UIBackgroundModes key with the voip value in your app’s Info.plist file.)
2、Configure one of the app’s sockets for VoIP usage.
3、Before moving to the background, call the setKeepAliveTimeout:handler: method to install a handler to be executed periodically. Your app can use this handler to maintain its service connection.
4、Configure your audio session to handle transitions to and from active use.
Including the voip value in the UIBackgroundModes key lets the system know that it should allow the app to run in the background as needed to manage its network sockets. An app with this key is also relaunched in the background immediately after system boot to ensure that the VoIP services are always available.
Most VoIP apps also need to be configured as background audio apps to deliver audio while in the background. Therefore, you should include both the audio and voip values to the UIBackgroundModes key. If you do not do this, your app cannot play or record audio while it is in the background. For more information about the UIBackgroundModes key, see Information Property List Key Reference.
For specific information about the steps you must take to implement a VoIP app, see Tips for Developing a VoIP App.
<!-- Image: /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/BackBoardServices.framework/BackBoardServices -->
<!-- #import <FrontBoardServices/FBSSystemService.h> -->
//debugserver About to launch process for bundle ID: com.mit.ss.backgroundApp
//[FBSSystemService][0xbd6c] Sending request to open "com.mit.ss.backgroundApp"
Received trusted open application request for "com.mit.ss.backgroundApp" from <FBProcess: 0x1704e9a00; debugserver; pid: 217>.
<!-- SpringBoard -->
Running <SBAppToAppWorkspaceTransaction: 0x10cfd02c0> for transition request:
<SBMainWorkspaceTransitionRequest: 0x1702e5f80; eventLabel: OpenApplication(com.mit.ss.backgroundApp)ForRequester(debugserver.217); display: Main; source: FBSystemService> {
applicationContext = <SBWorkspaceApplicationTransitionContext: 0x1706d6f80; background: NO> entities = {
SBLayoutPrimaryRole = <SBWorkspaceApplication: 0x17028fcd0; ID: com.mit.ss.backgroundApp; layoutRole: primary>;
};
}
<!-- mediaserverd -->
-CMSessionMgr- cmsmHandleApplicationStateChange: CMSession: Client com.mit.ss.backgroundApp with pid '218' is now Foreground Running. Background entitlement: YES
-CMSessionMgr- cmsmHandleApplicationStateChange: CMSession: Client com.mit.ss.backgroundApp with pid '218' is now Background Running. Background entitlement: YES
UIDebuggingInformationOverlay is a private UIWindow subclass created by Apple, presumably to help developers and designers debug Apple’s own iOS apps.
<!-- How to show UIDebuggingInformationOverlay -->
Call [UIDebuggingInformationOverlay prepareDebuggingOverlay]
Call [[UIDebuggingInformationOverlay overlay] toggleVisibility] - This shows the overlay window (assuming it’s not already visible).
<!-- One approach is to use the global ‘NSClassFromString’ and ‘NSSelectorFromString’ functions. In Swift, this approach looks something like:-->
let overlayClass = NSClassFromString("UIDebuggingInformationOverlay") as? UIWindow.Type
_ = overlayClass?.perform(NSSelectorFromString("prepareDebuggingOverlay"))
let overlay = overlayClass?.perform(NSSelectorFromString("overlay")).takeUnretainedValue() as? UIWindow
_ = overlay?.perform(NSSelectorFromString("toggleVisibility"))
<!-- The chief of these private classes, UIDebuggingInformationOverlay -->
http://ryanipete.com/blog/ios/swift/objective-c/uidebugginginformationoverlay/
<!-- https://github.com/DerekSelander/lldb -->
(lldb) po [UIDebuggingInformationOverlay prepareDebuggingOverlay]
(lldb) po [[UIDebuggingInformationOverlay overlay] toggleVisibility]
(lldb) exp -lobjc -O -- [UIDebuggingInformationOverlay _shortMethodDescription]
(lldb) methods UIDebuggingInformationOverlay
(lldb) image lookup -rn UIDebuggingInformationOverlay
> plutil -p MoneyDataStore.plist
1、IOS允许App的一个Socket在App切换到后台后仍然保持连接. 这个socket需要在应用第一次启动的时候创建, 并标记为"此socket用于VoIP服务". 这样当App切换到后台的时候,IOS会接管这个标记为"用于VoIP服务"的socket. 这个socket的响应函数(比如,一个delegate,或者是个block)会正常的响应, 就像App还在前台一样.
2、10s魔咒. 响应函数最多10s的时间来干你想干的事情
3、在socket的响应函数里, 你能通过NSLocalNotification来通知用户"电话来了"----既可以使用NSLocalNotification 进行通讯
4、允许在后台定期执行一段代码. 你可以设定一个大于等于10分钟的时间t, 和一个定期执行的handler, IOS系统会在每次经过t时间的时候调用一次这个handler. -----可以用来打开特定的app [[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"inf://"]]; //@"inf://"是你想要打开app注册的scheme,或者执行NSTask的 doShellCmd
5、我们通常用楼上的handler处理socket的断线重连操作
6、自启服务. 当IOS重新启动, 或者你的app因为其他原因退出时, IOS会马上启动你注册为voip的app, 你可以很迅速的恢复socket连接. 但是, 从底部多任务栏中手动关闭应用除外.更"code"的说明是:当程序退出的exitcode != 0,IOS会重启你的app.经试验发现,从底部多任务栏关闭的时候,程序的exitcode == 0.
7、当条目6描述的情况发生之后,app的application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:会被调用. 但是,请时刻提醒自己我们的app仍然处于后台. 我们以前总在这里创建window创建rootController, 但现在不必了. 现在我们需要的就是把可爱的socket连上, 像在条目1里一样,让一切回归正常
8、在application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:里你能通过[application applicationState] == UIApplicationStateBackground来判断是正常启动应用还是系统自动启动, 然后决定该创建window还是创建voip的socket.
<!-- 非越狱情况下实现: -->
1) 开机启动:App安装到IOS设备设备之后,无论App是否开启过,只要IOS设备重启,App就会随之启动;
2)无限后台运行:应用进入后台状态,可以无限后台运行,不被系统kill;
3)监听进程:可获IOS设备运行除系统外的App(包括正在运行和后台运行);窃取用户安装的app信息。
<!-- IT技术团队员工的特点 -->
一是希望完成任务之后能做自己的事情; 二是希望以自己的方式完成工作.------指定规则前, 征询大家的意见
<!-- 关于招聘的考量 -->
员工的本性很重要, 将来的塑造过程中很难改变.积极性和责任感是性格的一部分;
<!-- 关于员工塑造:需要明确每一个人的责任. -->
1、通常把员工看作是一员大将, 他们各自为团队镇守一方. 这样, 一个团队的战斗力才全面, 强劲.
2、另一个方面来讲, 一个人认为应该帮他(她)的人越多, 他的责任感就越小. 我们需要明确每一个人的责任.
3、 如果员工不明白自己的职责所在, 或者总认为自己可以部分责任,项目会走向失败.
<!-- 激发员工的责任感 -->
1、以身作则. 自己处处率先垂范,
2、光环理论: 如果你希望员工做到什么, 就要去表扬他们,好像他们已经做到了. 员工主动维护这个形象的力量是很大的.
<!-- 分清楚管与不管的界限 ----边界-->
1、一个典型的IT技术团队的管理者被授予的权利包括:绩效考核、晋升, 加薪, 解雇等方面的建议权。----对于员工的关心, 原则是只管工作, 不管生活.
2、 公生活可以谈论, 而且管理者应该主动关心公生活. 对于私生活, 即使员工主动提及, 也不要深入探究.
3、 应该尽量尊重他们的”领地”.
ps: 1)每个人的生活中, 有两部分, 一是普通的生活, 称为公生活: 例如身体不适, 孩子上学, 回家探亲, 周末逛街, 等等.
2)私密生活:包括宗教恋情, 婚姻状态, 性取向, 价值观, 人生观, 等等.
3)领地, 可以通俗的理解为”地盘”. 员工都有自己的”领地”, 比如座位空间, 其负责的工作, 等等.
<!-- 史玉柱说: 一定要尊重部下. 因为你这样做了, 他假如换个单位就碰不到这么好的领导. 所以遇到困难的时候他也不会走. -----切身体会-->
<!-- 考核 -->
在绩效考核的时候更要说得清楚, 否则, 会产生误解.
转载请注明:张坤楠的博客 > ImplementingaVoIPApp
在操作过程或者文章有问题的话欢迎在 原文 里提问或指正。